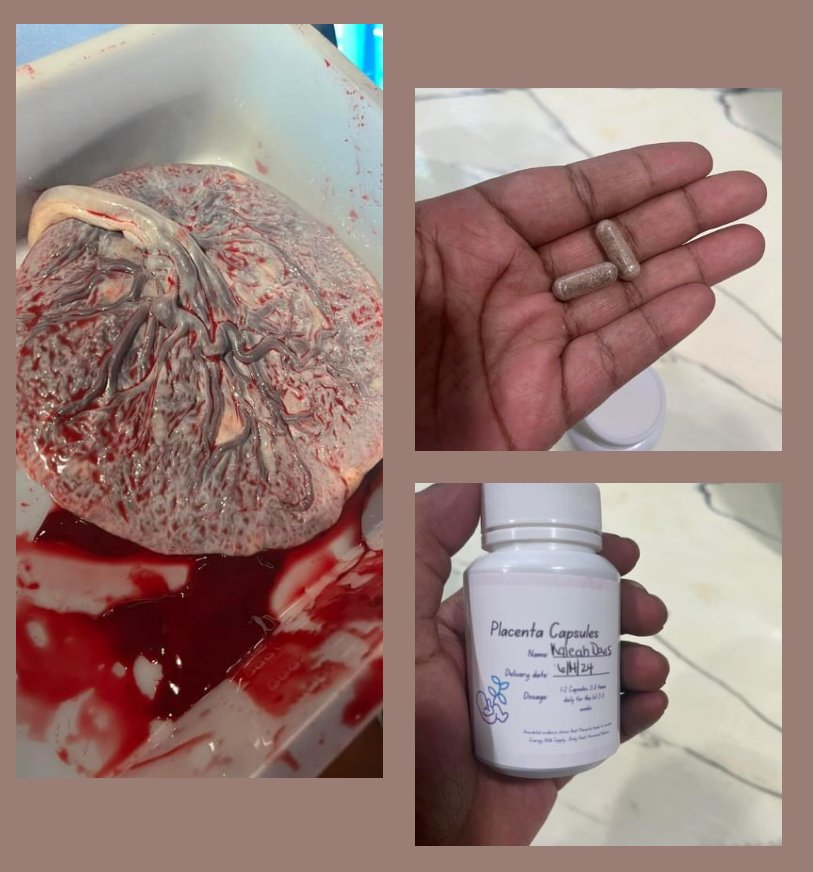
Understanding Placenta Benefits: Encapsulation, Tinctures & Salves
Traditionally used in some cultures, placenta encapsulation, tinctures, and salves are gaining interest among new mothers seeking natural postpartum support. While research is ongoing, many mothers find these practices beneficial.Let's explore what they are and their potential advantages.
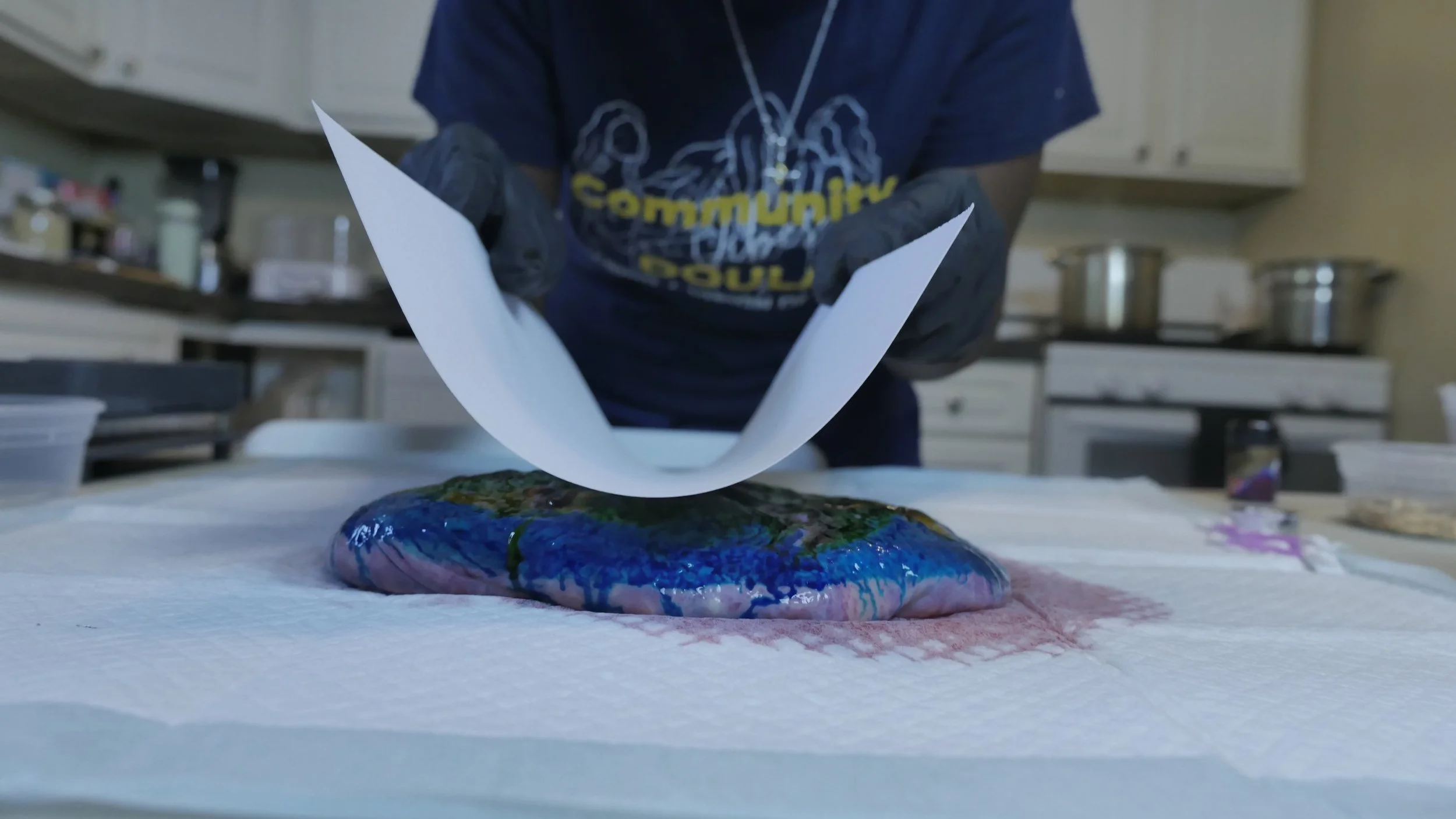
Placenta Encapsulation:
Process: The placenta, dehydrated and ground into a powder, is encapsulated into pills for oral consumption.
Potential Benefits:
Improved mood and reduced risk of postpartum depression [source]
Increased breast milk production [source]
Reduced postpartum fatigue and increased energy levels [source]
Pain management and uterine involution (shrinking back to pre-pregnancy size) [source]
Placenta Tinctures:
Process: The placenta is preserved in a concentrated alcohol solution, creating a tincture for later use (drops or spray).
Benefits over Encapsulation: Tinctures can last for years and address concerns beyond the immediate postpartum period.
Potential Benefits:
Similar benefits to encapsulation during postpartum period
Easing symptoms of PMS and menopause [source]
Supporting emotional well-being during stressful times [source]
Placenta Salves:
Process: The placenta is infused into a base like oil or shea butter to create a topical salve.
Potential Benefits:
Soothing skin irritations like perineal tears or hemorrhoids [source]
Promoting skin healing after childbirth (c-section scars, etc.) [source]
Reducing diaper rash discomfort in babies [source]
Important Considerations:
There is limited scientific research on the efficacy of these practices.
Always consult with a healthcare professional to discuss if these practices are right for you.
Ensure proper preparation procedures are followed to avoid potential health risks.
Additional Resources:
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG): source about postpartum depression
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice.